Know how your numbers are key to your health.
What are the key numbers in your life? I just turned 50. That is a number that seems like a real turning point. I like a viewpoint a friend shared with me: the first half-century is training and preparation for the better half!
Also, my daughter is graduating from high school. So, in her world the key numbers are GPA, SAT, ACT, and college fees.
Other numbers we keep close to us are phone numbers, bank balances, addresses, and birthdays.
Numbers and Health
Now I want to make sure you are aware of key numbers for your health. There is a reason for those labs at your annual physical. And there are goals for those numbers. When you see your lab results you will see your number and a range that contains all of the normal numbers. Ideally, your number falls in this range. If your numbers are little bit outside this ‘normal range’ for a little while, just talk with your doctor. If your numbers stay outside the range, your doctor will probably take action with medication, exercise changes, diet changes, or other plans.
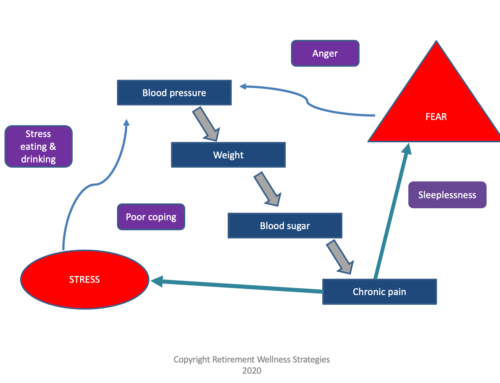
Blood pressure – If you are under age 65, normal is less than 140/90. If you are over 65, some experts agree it’s ok for your systolic blood pressure (top number) to get as high as 150. Your blood pressure is one indicator of how hard your heart has to work. There are several medications that can be used to lower your blood pressure and protect your heart from having to work too hard. I am often asked about how low is too low for your blood pressure. That is not really determined by a number. It is found through symptoms. If you get really dizzy when you stand up, turn around, or try to walk faster, talk with your doctor. A little bit of this is expected with the medicines that are protecting your heart. If it is causing you to fall or keeping you from doing your normal activities, then let your healthcare team know.
Pulse – This is usually between 60 and 90 beats per minute. You can quickly check your own by touching the center of your neck and letting your fingertips slide to the soft area just to the side. Your carotid artery is there, and you can count the beats for 15 seconds then multiple by 4. The more you exercise, the more efficient your heart gets. So, really fit people tend to be at the bottom of this range. This should be measured when you are really at rest. If you are worried, in pain, stressed out, or in a conversation your heart rate will be higher. So, when this is measured, think quiet thoughts and don’t talk. If it gets and stays high, your doctor will order some more tests to check why. The same is true if your heart rate is slower than 60 beats per minute. Tests will be ordered to see what your heart is doing to cause the slow rate.
Cholesterol – We all have cholesterol, or fats, in our blood. This is normal. But there are healthy amounts and unhealthy amounts. These are the key numbers. For most people, your low density lipoproteins (LDL) number should ideally be under 100 mg/dL. If you have a strong history of heart disease, your doctor might have you try to reach an even lower goal. This is your ‘bad cholesterol’. Your high density lipoproteins (HDL) is your ‘good cholesterol’. Ideally you want this number to be over 40 mg/dL. Another cholesterol number is your triglycerides. This tends to go up if you have diabetes that isn’t well controlled. This number should be less than 150 mg/dL. Diet, exercise, and medications are all key in keeping these numbers in the goal range if you have high cholesterol (also called hyperlipidemia).
Blood sugar – Speaking of diabetes, this is a very important number for people with diabetes. It is important whether you have type 1 (requires insulin) or type 2 diabetes (can be treated with medicines you take by mouth, by inhalation, or by injection). Your blood sugar changes throughout the day. It is usually lowest before a meal and highest after. When you have not eaten for at least 8 hours, your blood sugar should be less than 100 mg/dL. (This is a ‘fasting blood glucose’.) Your healthcare team might ask you to measure your blood sugar at home. There are several types of monitors to do this. They might want you to check sometimes before you eat, sometimes after you eat, sometimes before bed, and sometimes when you first wake up. This will give them the best look at what your blood sugar does throughout the day.
Glycosylated hemoglobin (A1c) – This is another way to see what your blood sugar does over a period of time – about 3 months. It is a reflection of your average blood sugar over those months. People who do not have diabetes have an A1c under 6%. Current guidelines encourage a goal of less than 6.5% for people with diabetes. However, if someone is at risk for their blood sugar being too low your doctor might increase this goal closer to 7%. When people with diabetes also have other medical conditions, sometimes ‘tight control’ to under 6.5% is not possible or safe. Talk with your healthcare team for your specific goal and why that is the goal for you.
Body Mass Index (BMI) – This measurement is a reflection of your height, your weight, and your gender. It helps to define what is a healthy weight for you. The goal BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9. If your BMI is 25 to 29.9 you are overweight. If it is over 30 then you are obese. Your healthcare team will help you with a plan to get to a healthy weight and stay in that healthy range.
Blood Urea Nitrogen and Serum Creatinine (BUN and SCr) – These are important measures of your kidneys. They determine if your kidneys are clearing extra fluid, medications, and toxins from your body as they should. They can also tell your doctor if you are dehydrated from not drinking enough. As a pharmacist, I always look at these numbers when deciding if a medication is safe and at the right dose. When your kidneys are not working as they should, then it is hard to get some medications back out of the body. Another interesting numbers – Our kidneys start to very gradually slow down when we are in our late 30’s or early 40’s. This happens to everyone. So, with each birthday in our 50’s and beyond, these are important numbers to assess.
Aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (AST and ALT) – These are measures of how your liver is working. Many medications are metabolized (broken down) in the liver. If these numbers are very high, then the liver is not able to do its job to break down the medication. These are numbers I always look at when evaluating someone’s medication regimen. It helps determine what medicines should be avoided and what doses are best for you based on your liver.
Number of Medications – Sometimes several medications are needed to treat all of your medical conditions. Sometimes they are not. The more medications someone takes, the more risk of medications interacting and causing problems rather than helping them. There is no ‘magic number’, but most experts agree that taking more than 4 medications regularly means you need to have an expert very carefully evaluate your regimen. This is to double check that your medication regimen is providing optimal good with minimal risk.
An Evaluation of YOUR Numbers
Are you curious about your numbers? At Meds MASH we specialize in these evaluations, especially in anyone over age 60. Do you want to better understand your particular numbers? Do want to know that your medicines are providing optimal good and minimal risk? Call us today! We have found that over 50% of our clients need a medication adjustment once an expert evaluation is done. These adjustments come from your own doctor with our collaboration.
You can call for your appointment at 410-472-5078 or e-mail at michelle@medsmash.com or through our website www.medsmash.com/contact.
For further application, check out my personal blog.