Follow these steps to prevent sudden confusion in the hospital like a series of falling dominoes.
Growing up I played countless games of Dominoes with my grandparents. And of course, the other fun thing to do with Dominoes is line them up and watch them fall is some funky pattern.
Hospitalization and memory or behavior changes
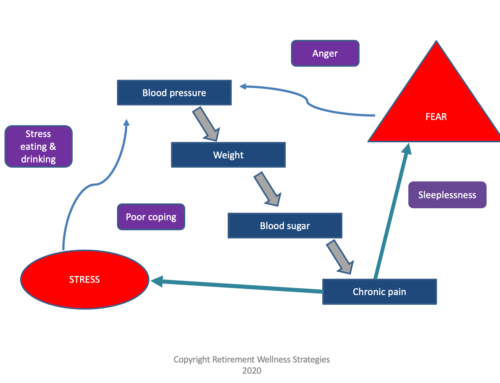
Many times in my career I have seen people experience a sudden decline in their health, often around a hospitalization. The general theme that I see far too often resembles falling dominoes and goes something like this:
- Someone has a reason to go to the hospital
- A medication is given that makes the person confused
- An assumption is make this person has some form of dementia
- That diagnosis is added to the record
- With the confusion, behaviors change (crying out, pulling at IV’s, getting out of bed)
- By the way, this is very alarming for the family and friends
- More medications are added to control the behaviors
- The person now truly looks like someone with advanced dementia
- Unable to safely walk
- Unable to clearly think and answer questions
- Unable to care for him/herself
- The person cannot return home and to the independent life led before the hospitalization
- The person is sent on to rehabilitation or assisted living or skilled nursing care
- The diagnoses and the medication go with them and are continued for the rest of life
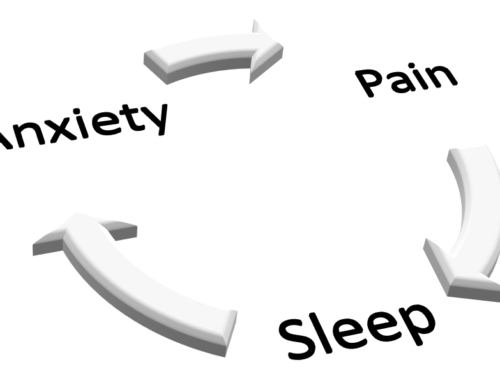
In this scenario there might have been some early cognitive decline (early signs of some sort of dementia). The move to the unfamiliar environment with the scurry of activity and then the altered schedule can ‘unmask’ that early dementia and make it seem suddenly incredibly worse. Add an infection or painful condition, and this is even worse still. It could also be a sign of delirium (a short term confused state). That DOES NOT mean this confused state is the way this person will stay. Some of the best actions at this point are to dim the lights, quiet the person’s room, keep someone dear close by to assure the person that all is ok. This quieter reassuring environment can help reduce the confusion and behavior changes.
Elective procedures
Another all-to-familiar scenario is similar:
- A person has an elective procedure
- Part of the sedation and anesthesia for the procedure makes the person confused and disoriented
- Any cries out or uncoordinated behaviors are interpreted as pain
- More pain medication is given
- When the person goes to rehabilitation or back home to recover, a schedule pain regimen is included
- Rather than moving and doing all of the exercises that will enable rapid and full recovery, the person is too sedated from the pain medication and sleeps
- The lack of post procedure stretching, movement, and exercises prescribed by physical therapy limit the range of motion and full recovery from the procedure
- For the rest of life the person has limited use of the limb/joint due to lack of use right after the procedure
How can you better navigate these scenarios?
If there have been any signs of memory changes, know that you might see this sudden confusion. Also, it seems the more critical the admission the higher the risk of delirium. (So, accidents, being in critical care, being placed on a ventilator, and such carry the higher risk).
Talk with the healthcare team about taking the following steps:
- Dim the lights
- Have a private room/space that stays as quiet as possible
- Keep someone reassuring nearby
- Keep glasses and hearing aids on to help with orientation
- Have a clock and date information visible
- Assure there is no infection (can cause confusion and behavior changes)
- The healthcare team can make sure no medications are being used that can alter thinking.
- If there is a sudden change in your loved one, stay calm. Delirium goes away with time and with these calming steps.
- Ask for the minimum amount of pain medication to be given to limit the associated confusion and sedation.
The goal is to take care of the problem that led to the hospitalization without delirium or other confusion. Let those dominoes say standing.
For more information about delirium and steps you can take to prevent or resolve it, contact us at www.medsmash.com/contact.
For further application, check out my personal blog.